



How to select the size of electric cable
Wire is used to carry current from the battery through the vehi- cle to various electrical components: lights, instruments, etc.
In automotive use, the grounded return system is used almost exclusively. In this system, a single wire is run from the battery through switches to the load and the vehicle itself provides the ground or return to the battery.
It is important to note that all electric components have a good ground. In a combination of vehicles (tractor-trailer) it is important that a good and adequate size ground wire be pro- vided between the two vehicles to carry the current.
Wire has certain resistance to current flow. The smaller the wire, the greater the resistance.
Also, as the amount of current (amps) increases, the resis- tance (ohms) increases.
For a 12-volt system there are two factors to be considered:
The Wire Size charts shown below are provided for easy selection of wire sizes. These charts, however, neglect losses due to connections or switches. To use either of these charts:
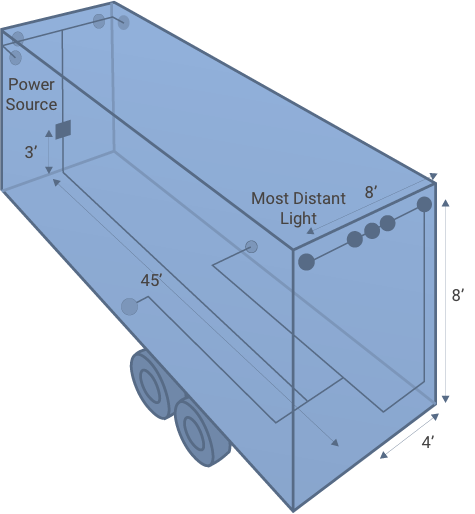
Add 2 feet for connections and slack to reach around obstacles.
Wire Length Calculation:
3+45+4+8+8+2 = 70 feet
Example
On a 12-volt system, operating at an ambient temperature of 125° F, determine the wire size required for a clearance light circuit having eleven lights using No. 97 bulbs
WIRE SIZE CHART |
|||||||||||
For A 12-Volt System |
For A 6-Volt System |
Length of Wire (Most Distant Light) |
|||||||||
10’ |
20’ |
30’ |
40’ |
50’ |
60’ |
70’ |
80’ |
90’ |
100’ |
||
Load in Amps |
Load in Amps |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
Wire Gauge |
1.0 |
0.5 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
1.5 |
0.75 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
2.0 |
1.0 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
3.0 |
1.5 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
14 |
14 |
4.0 |
2.0 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
16 |
16 |
14 |
14 |
14 |
12 |
5.0 |
2.5 |
18 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
14 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
6.0 |
3.0 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
16 |
14 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
7.0 |
3.5 |
18 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
8.0 |
4.0 |
18 |
16 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10.0 |
5.0 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
11.0 |
5.5 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
12.0 |
6.0 |
18 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
8 |
15.0 |
7.5 |
18 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
18.0 |
9.0 |
16 |
14 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
20.0 |
10.0 |
16 |
16 |
12 |
12 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
TEMPERATURE CHART |
|||
Cable Size |
Maximum Current Carrying Capacity (For 12 Volts at Listed Temperatures) |
||
120° F |
125° F |
150° F |
|
20 Gauge |
15 Amps |
13 Amps |
9 Amps |
18 Gauge |
18 Amps |
15 Amps |
11 Amps |
16 Gauge |
22 Amps |
19 Amps |
14 Amps |
14 Gauge |
27 Amps |
23 Amps |
17 Amps |
12 Gauge |
40 Amps |
32 Amps |
24 Amps |
10 Gauge |
50 Amps |
42 Amps |
31 Amps |